What is Soybean Oill ?
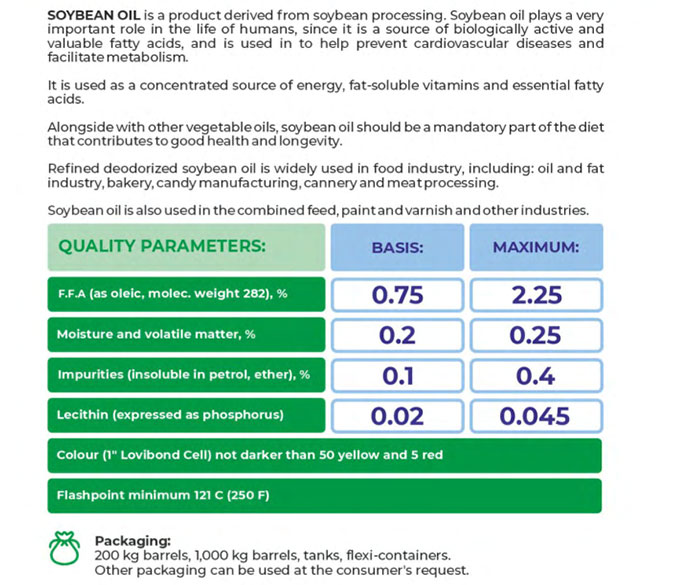
Soybean oil is extracted from the soybean (Glycine max) and often has a dark yellow or faint green color. Standard vegetable oil is typically composed of soybean oil. The first domestic use of soybean is traced to the eastern half of North China in 11th BC, or perhaps a little earlier. Soybean is one of the five main plant foods of China, along with rice, wheat, barley, and millet. Early accounts have it that soybean production was localized in China until after the China-Japan War of 1894 to 1895, when the Japanese started to import soybean oil cake as fertilizer.
Other uses
Soybean oil is processed and sold mainly as a vegetable oil, while the remaining soybean meal is typically used as animal feed. It is also the primary source of biodiesel in the country, making up 80 percent of domestic production. Lecithin is a product extracted from soybean oil, and it is a natural emulsifier and lubricant used in many foods and commercial and industrial applications. It helps keep the chocolate and cocoa butter in a candy bar from separating, and is used in pharmaceutical products and protective coatings.
Benefits of Peanut Oil
Benefits in cooking with Peanut Oil
– Very high burn point (232 degrees, Celsius), so it lasts longer and is more stable when cooked with under high temperatures
– High in monounsaturated fats that help reduce bad LDL High in vitamins A, D and E
– As healthy as olive oil which is regarded as healthiest oil.
– Naturally so good it can be consumed as virgin oil in raw form Triple refined,
– Odourless and durable
– No artificial additives added Cost-effective
Perhaps the most interesting thing about the peanut is that it isn’t a nut at all. It’s actually a legume, in the same family as lentils, peas and beans. They are also known as groundnuts because after the pea-like flowers wither, the stem pushes underground and buries the developing peanuts. These super pint-sized nuts are a very good source of monounsaturated fats, the type of fat that is emphasized in the heart-healthy Mediterranean diet. Studies of diets with a special emphasis on these nuts have shown that this little legume is a big ally for a healthy heart. In addition to their monounsaturated fat content, they feature an array of other nutrients that, in numerous studies, have been shown to promote heart health. They’re also good sources of vitamin-E, niacin, folate, protein and manganese. Not only do peanuts contain oleic acid, the healthful fat found in olive oil, but new research shows these tasty legumes are also as rich in antioxidants as many fruits. While unable to boast an antioxidant content that can compare with the fruits highest in antioxidants, such as pomegranate, the roasted variety do rival the antioxidant content of blackberries and strawberries, and are far richer in antioxidants than apples, carrots or beets.
Other uses
Orally, peanut oil is used to lower cholesterol and prevent heart disease. It is also used orally to aid in weight loss and decrease appetite, and to help prevent cancer. Topically, peanut oil is used for arthritis and joint pain, scalp crusting and scaling without hair loss, dry skin, eczema, and ichthyosis (non-inflammatory skin disorders that cause scaling). Rectally, peanut oil is used in ointments and medicinal oils for treating constipation. It is also used as a vehicle for external, enteral, and parenteral pharmaceutical formulations. Eating peanuts just two or more times each week was associated with a 58% lowered risk of colon cancer in women and a 27% lowered risk in men. In manufacturing, peanut oil is used in skin care products and baby care products.
What is the allergen in peanuts?
What about peanut oil?
Refined peanut oil did not pose a risk to any of the subjects. British Medical Journal, 2006
The fact is that highly refined peanut oil is different from peanuts, peanut butter, and peanut flour when it comes to allergy. This is because most peanut oil undergoes a refining process, in which it is purified, refined, bleached, and deodorized. When peanut oil is correctly processed and becomes highly refined, the proteins in the oil, which are the components in the oil that can cause allergic reaction, are completely removed, making the peanut oil allergen-free.
Speciality Oil Variety of quality oils, such as: Cotton Seed oil, Macadamia Oil, Almond Oil, Coconut Oil and Hemp Seed Oil are in a range of production on dedicated buyers request

Palm Oil
Palm Oil
Palm Olein
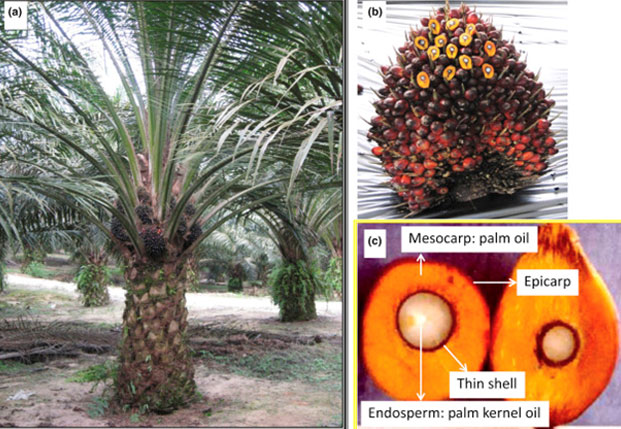

Main Difference
Although palm oil and palm olein are produced from the same plant and share many similar properties,
the main difference between them is their chemical state at room temperature. Semi-solid palm oil is used more frequently as a fat in bakery products, whereas liquid palm olein is considered the “gold standard” and is the most widely used oil for frying in the world.
Vegetable Oils And Fats